Site Navigation
Home
All rocks contain uranium, although most contain just a small amount. Certain types of rock, including granite, dark shale, light-colored volcanic rocks, sedimentary rocks containing phosphate, and metamorphic rocks derived from these rocks, have higher than average uranium content.
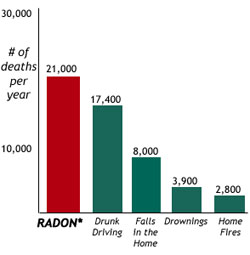
Radon is the largest source of exposure to naturally occurring radiation. It is a common misconception that certain areas of the United States are not at risk for radon. In fact, high levels of radon have been reported in all 50 states. Indoor radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
High radon levels in a home is considered dangerous because of the link from radon exposure to lung cancer. Radon, an inert gas that is colorless and odorless, is highly radioactive. The radioactive particles produced from the decay of radon can get lodged in one's lungs, and potentially cause fatal health problems. Detecting radon has become of great importance, and the EPA recommends that EVERYONE test their home for radon. By taking this course, you will know how to measure amounts of this dangerous gas, and how much is considered hazardous. You will have the ability to help those who may be living with a fatal substance in their homes.
Radon Information
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that is colorless, odorless, and tasteless--rendering it unable to be detected by the human senses. It is produced as a result of the natural decay of uranium in soil, rock and water. Uranium is common in the environment and some amount can be found in each of the 50 states.All rocks contain uranium, although most contain just a small amount. Certain types of rock, including granite, dark shale, light-colored volcanic rocks, sedimentary rocks containing phosphate, and metamorphic rocks derived from these rocks, have higher than average uranium content.
Radon is the largest source of exposure to naturally occurring radiation. It is a common misconception that certain areas of the United States are not at risk for radon. In fact, high levels of radon have been reported in all 50 states. Indoor radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
High radon levels in a home is considered dangerous because of the link from radon exposure to lung cancer. Radon, an inert gas that is colorless and odorless, is highly radioactive. The radioactive particles produced from the decay of radon can get lodged in one's lungs, and potentially cause fatal health problems. Detecting radon has become of great importance, and the EPA recommends that EVERYONE test their home for radon. By taking this course, you will know how to measure amounts of this dangerous gas, and how much is considered hazardous. You will have the ability to help those who may be living with a fatal substance in their homes.

